NTFS short for New Technology File System is the default file system in Windows system, which is a very reliable file system. But, like any other file system, it can also get corrupted.
What should I do if my NTFS file system gets corrupted? Is the data on the volume lost too? Well, do not worry. In this article, we will explain, how you can easily and safely recover your lost data by employing some simple methods.
Now the most important thing in this situation is recovering your data, The causes of corruption, and preventive measures can be discussed later. So let us get right into recovery methods.
Recover Data from Corrupt NTFS File System
Many methods can be employed, to recover data from corrupt NTFS file systems. But, their effectiveness, ease of use, and safety may vary. We have compiled the most effective, easy-to-use, and safest methods. Let’s take a look.
Fix 1: Boot into Safe Mode
Since safe mode loads the operating system with minimal drivers many times it can file system errors like corruption of NTFS and you can access your data. From here, simply copy the data to an external storage device. However, this method may not work in case of severe file corruption.
To boot into safe mode follow the steps
- Press Windows + R type msconfig and press Enter.
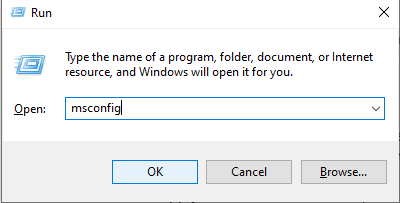
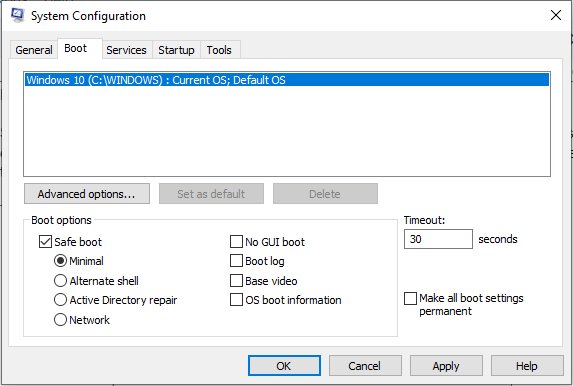
- Navigate to the Boot tab check the box Safe mode and select the option Minimal (Network if you also want internet access).
- Click on Apply and then restart the computer to boot it into safe mode.
If you are not able to access your data move on to the next method.
Fix 2: Fix Corrupt NTFS volume by CHKDSK
You can utilize CHKDSK which is an in-built utility to check drives for errors. Follow the steps as shown below to use this utility.
- Press Windows + R and type cmd. Press Shift + Ctrl + Enter, to run the command prompt as Administrator.
- In the command line enter the command chkdsk D: /f /r (replace D by the drive letter on which the corrupt NTFS volume is present).
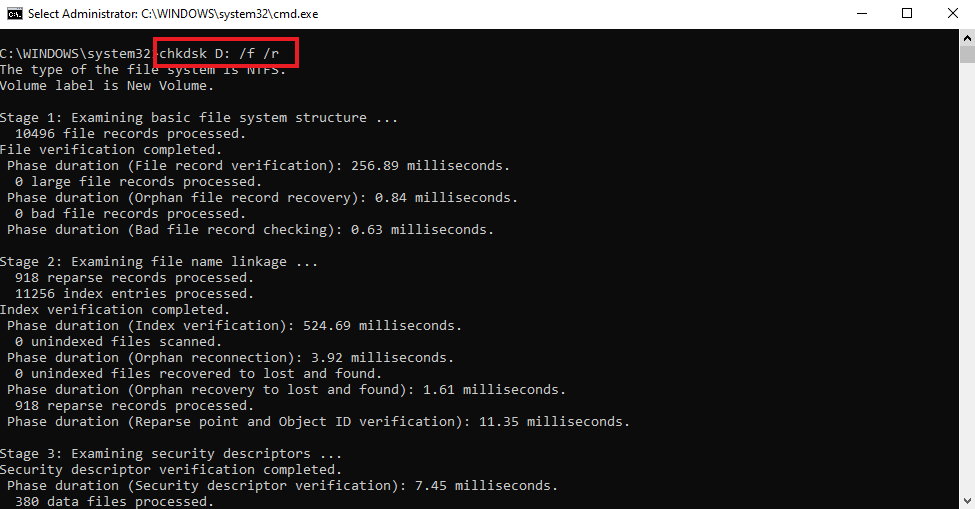
Note: You can also use chkdsk while in the Safe Mode. Use this in case, the system is crashing.
If this does not work move on to the next method.
Fix 3: Boot using Linux Live
Sometimes, corruption issues that are specific to the Windows environment may be present, which prevents Windows from accessing the NTFS partition. In such a case, booting into a different OS may bypass the corruption and you will regain access to the partition.
Linux is a suitable OS for this task as it is easy to boot into Linux. Most Live Linux distributions support read-only access to NTFS partitions.
Steps to Boot into Live Linux
- Choose the Linux Distribution: Choose the Linux Distribution of your choice like Ubuntu, Mint, or any other distribution.
- Download the ISO file: Most Linux distributions have a downloadable ISO (Disc Image) file, which contains the installation files for the said OS. Download the ISO file for the distribution of your choice.
- Create bootable media: The next step involves creating bootable media. This can be a USB, CD/DVD, external HDD or SSD. You can use programs like Rufus or Balena Etcher free, open-source, and user-friendly utilities, that can take ISO files and create bootable media.
Note: The data on the device that you use to create a boot media will be erased, so make sure you backup your data before using it as boot media.
- Boot from the Boot media created: Boot into Live Linux by using the boot media created This involves restarting the computer and entering the BIOS or UEFI settings. The steps may differ for different computers. Check the manual for specific steps.
- Access the NTFS partition: Once you are booted into the Live Linux environment, open the file manager and go to the Devices or Computer section. You should see your computer’s hard drives. Find the partition you want to access and double-click on it to Mount it.
- Copy Data to External Hard Drive: Once mounted you should be able to access your data. Copy the data to an external hard drive.
- Unmount the Partition: Before restarting the device make sure that you unmount the NTFS partition. You can do this by right-clicking on the partition and selecting the option Eject or Unmount.
- Restart the computer: Once you have copied the data, shut down the computer, remove the Live Linux Boot media, and restart your computer to boot into your Windows OS.
If this method does not work for you either, we would recommend going for professional Data Recovery software. CAT Data Recovery software is one such tool that is a fast, efficient, and safe tool. Download it for free and try it for yourself.
Fix 4: Use CAT Data Recovery to Recover Data from Corrupt NTFS File System
You can use CAT Data Recovery software under various scenarios of data loss, whether it is due to corruption, deletion, formatting, or some errors. Using this tool you can recover data from a crashed system let alone a corrupt NTFS file system.
To use this tool follow the steps.
- Download and Install CAT Data Recovery software. Open the application.
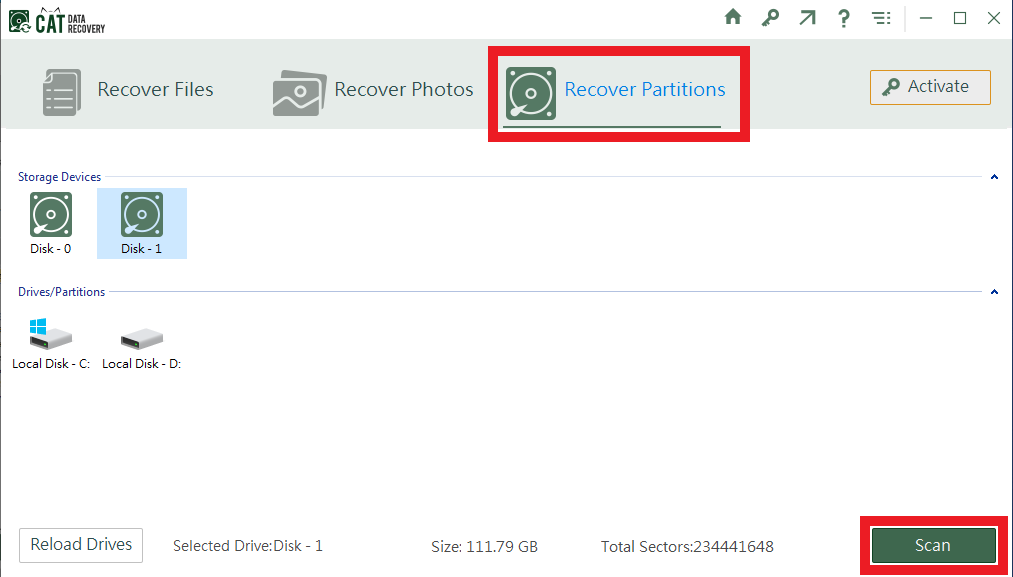
- Go to the Recover Partitions tab, and select the disk where the corrupt NTFS volume was present. Click on Scan.
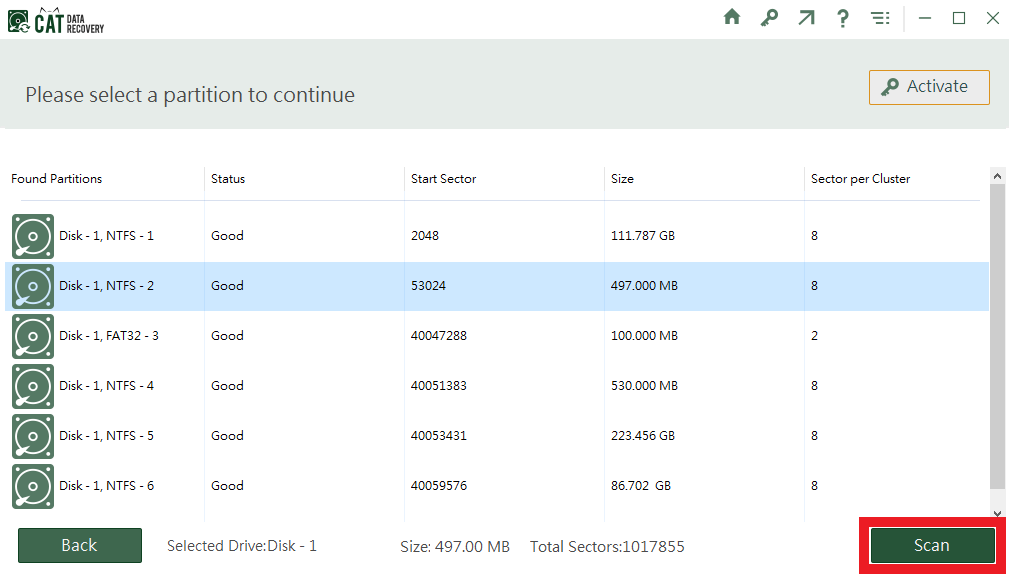
- On completion, all the partitions on the disk will be visible. From the list select the corrupt NTFS partition. Click on Scan.
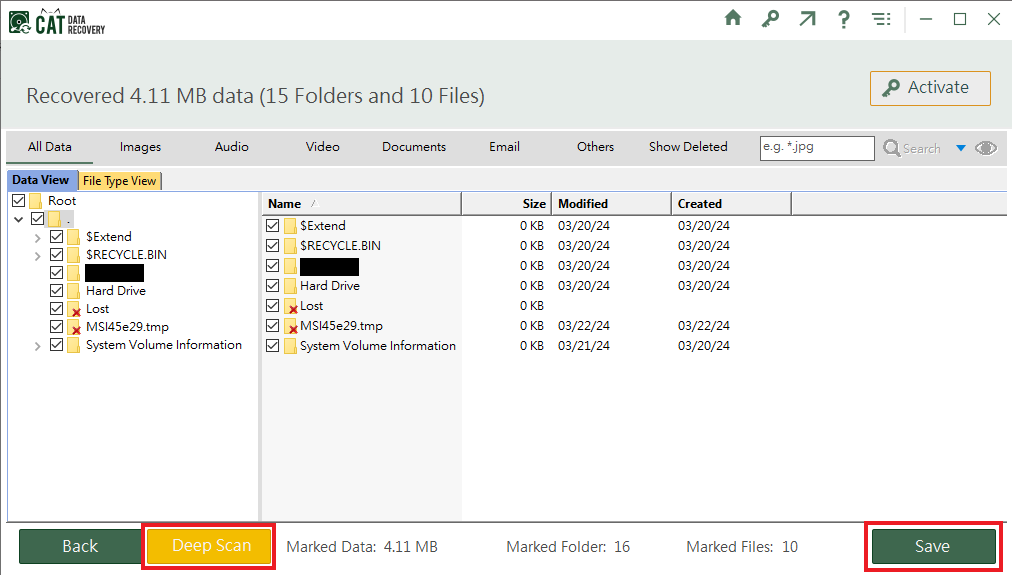
- After completion, all the data on the volume will be visible.
- If the data you want to recover is not showing select the option Deep Scan for a more thorough scan. Once satisfied, select the data you want to recover and select Save to recover it.
After recovering the data reformat the NTFS partition to remove corruption.
Conclusion
We hope that you will now be able to safely recover your data from any corrupt NTFS file system. If you find this article helpful, share the article with others.